Create - Landscape
It creates the rough mesh of landscape from an image file or fractal image.

It works for the currently selected object. (You can select the current object on Object Panel.)
It creates the rough mesh of landscape from an image file or fractal image.

It creates strings using TrueType font. You can specify a smoothness, a size and a thickness for a text.
It entirely polygonizes the current object on which the patch or mirror is applied.
All objects will be frozen when you select this menu with Shift key.
 |
 |
 |
| Before | After |
It arranges the current object at the position which is designated by the direction of each axis.
When you use [Snap to ground (Y=0)], the bottom of the object will be snapped to the ground.
 |
 |
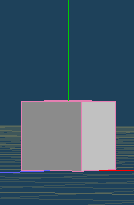 |
| Before | After [Snap to ground (Y=0)] |
It joins the closed vertices in the same object.
It is mainly used to join vertices which seem to be close by appearance but they really are separated.
It reduces the vertices of the current object without changing the appearance.
You can select an algorithm of reducing from [Fast] or [Specify number].
You can confirm the result in advance by pushing [Preview].
 |
 |
 |
| # vertices : 1054 | # vertices : 300 |
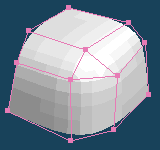
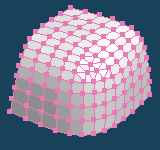
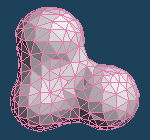
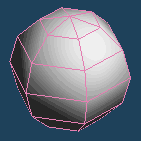
It makes faces more smooth by dividing each face. It sometimes becomes roughly.
 |
 |
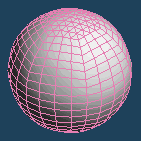 |
| Divide faces by Segment:4 | ||
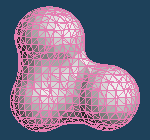
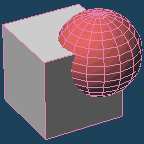
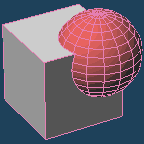
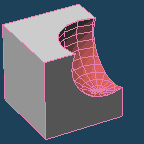
It executes a boolean operation to [Union], [Subtract] or [Intersect] between a base object and a target one.
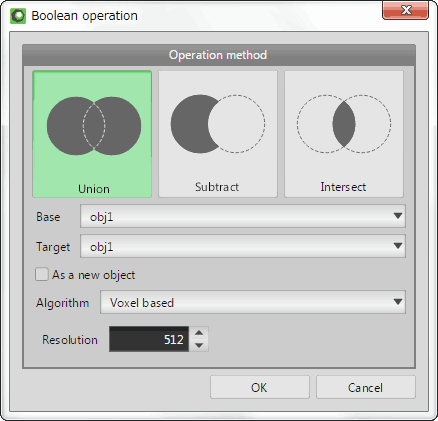
| An initial shape | ||
 |
||
| [Base] is the gray cube, and [Target] is the red sphere. They are intersected each other. | ||
 |
||
| Union | Subtract | Intersect |
 |
 |
 |
| The [Base] object and the [Target] object is merged. |
The [Base] object is subtract by the [Target] object. |
The overlapped part between the [Base] object and the [Target] one is extracted. |
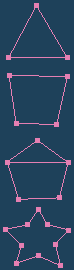
A face will be created in the part surrounded by three or four lines. A face is not created in the par surrounded by five or more lines. The current material is assigned to the new faces.
 |
 |
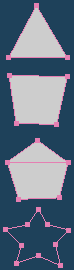 |
| Original | After |
It aligns the direction of faces in the current object.
But, whether they turn to the inside or the outside is not fixed, you may need to use [Invert].
And you cannot unify them well without closing all faces to one perfectly.
It deletes one of the faces in case two faces are located on the same position in the current object.
It deletes one side of faces which have both front and back sides in the current object. As which side will be deleted is unknown, you may need to use [Align faces].
Nothing is done with a double-sided face by [Material Property] because there is one face only.
It attaches the current material to the non-material faces in the current object.
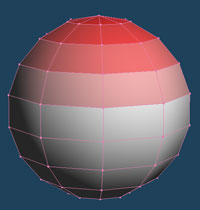
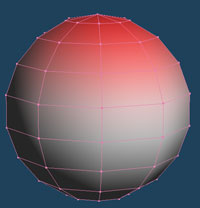
It displays the direction of each face as a vertex color. You can select a type of a direction to colorize, and a unit to apply.
The [Vertex color] must be active in the [Material Panel] when you colorize the normal. Please notice that it is not active, the color will not be displayed.
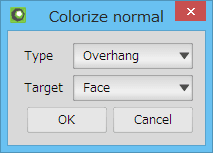
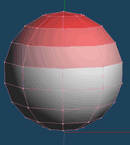
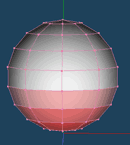
| Up face | Overhang | XYZ normal |
 |
 |
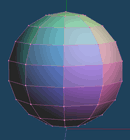 |
| It appears red is emphasized as directed above | It appears red is emphasized as directed under | X axis is red, Y axis is green and Z axis is blue. |
| Face | Vertex |
 |
 |
It converts polygon objects to voxel and you can edit it.
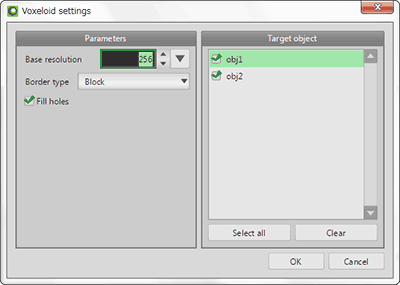
Select target objects from list and click [OK], converted voxel objects are displayed on voxel view.
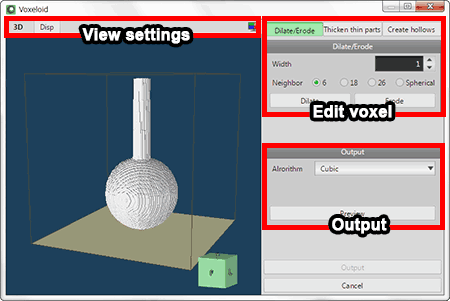
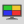

 |
 |
 |
| Dilate to Width:10, Neighbor:6 | ||
 |
 |
 |
| Target width:15, Thicken width:10 | ||
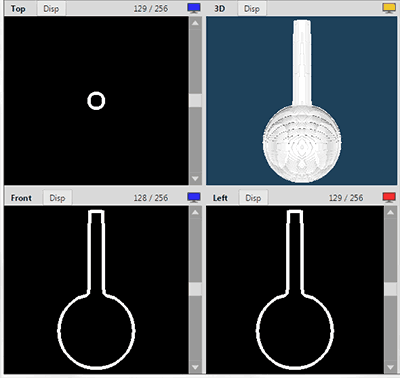
It solidifies a texture on an object. You can solidify with two methods; texture emboss and transparency; by setting a mapping image as [Texture] or [Alpha] in [Config] of [Material Panel].


 |
 |
 |
| Original | Solidify front texture emboss |
 |
 |
 |
| Original | Solidify double sided texture emboss |
Convert solidify objects to polygon and output.
Click [Preview] and check converted result. Then, click [Output] and create as new objects.
You can reduce faces of the objects by remeshing, if faces of the object increase too many.
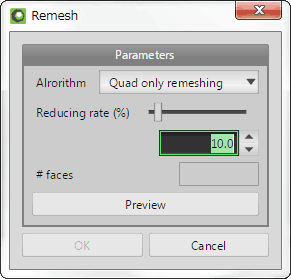
Click [Preview] and display the remeshed object. The number of faces after reduction is displayed in the [#faces]. Then, click [OK] and create as new objects.
It makes all edges of faces to lines and deletes faces.
It deletes all lines in the object.